This Configuration Guide shows how to configure a GRE tunnel within an IPsec connection.
Situation
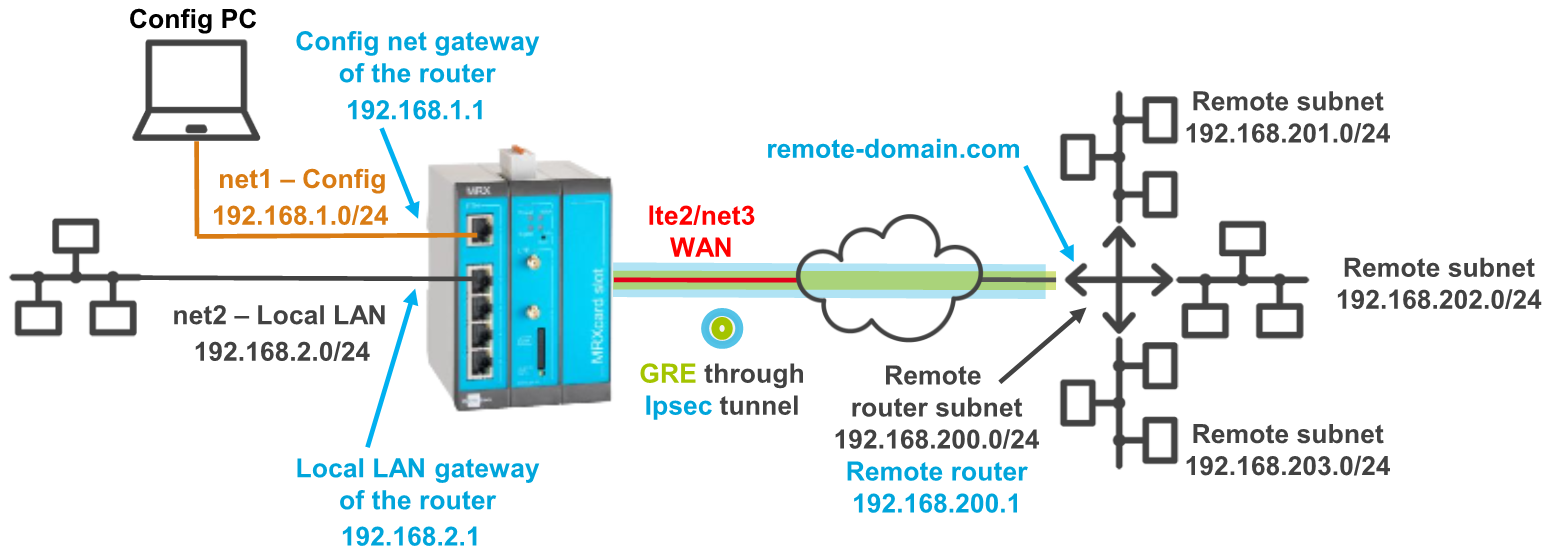
A remote router has several local subnets that need to be addressed from the INSYS router. An IPsec connection only allows to address one subnet. A GRE connection can be established to more than one subnet, but cannot be encrypted. To be able to establish encrypted connections to more than one subnet, it is possible to route a GRE tunnel through an encrypted IPsec connection.
Solution
It is prerequisite that you have access to the web interface of the router and the router is configured for a WAN connection using the startup wizard from default settings. It is also prerequisite that the remote router supports GRE via IPsec. The following figure shows the network topology that is used for this example:
Keep your router up to date!
Update your router to iom OS 7.3 or later first! All encryption algorithms that are no longer considered sufficiently secure have been removed starting with this version, which eliminates the possibility of such algorithms being used inadvertently.
Open the user interface of the router: https://insys.icom
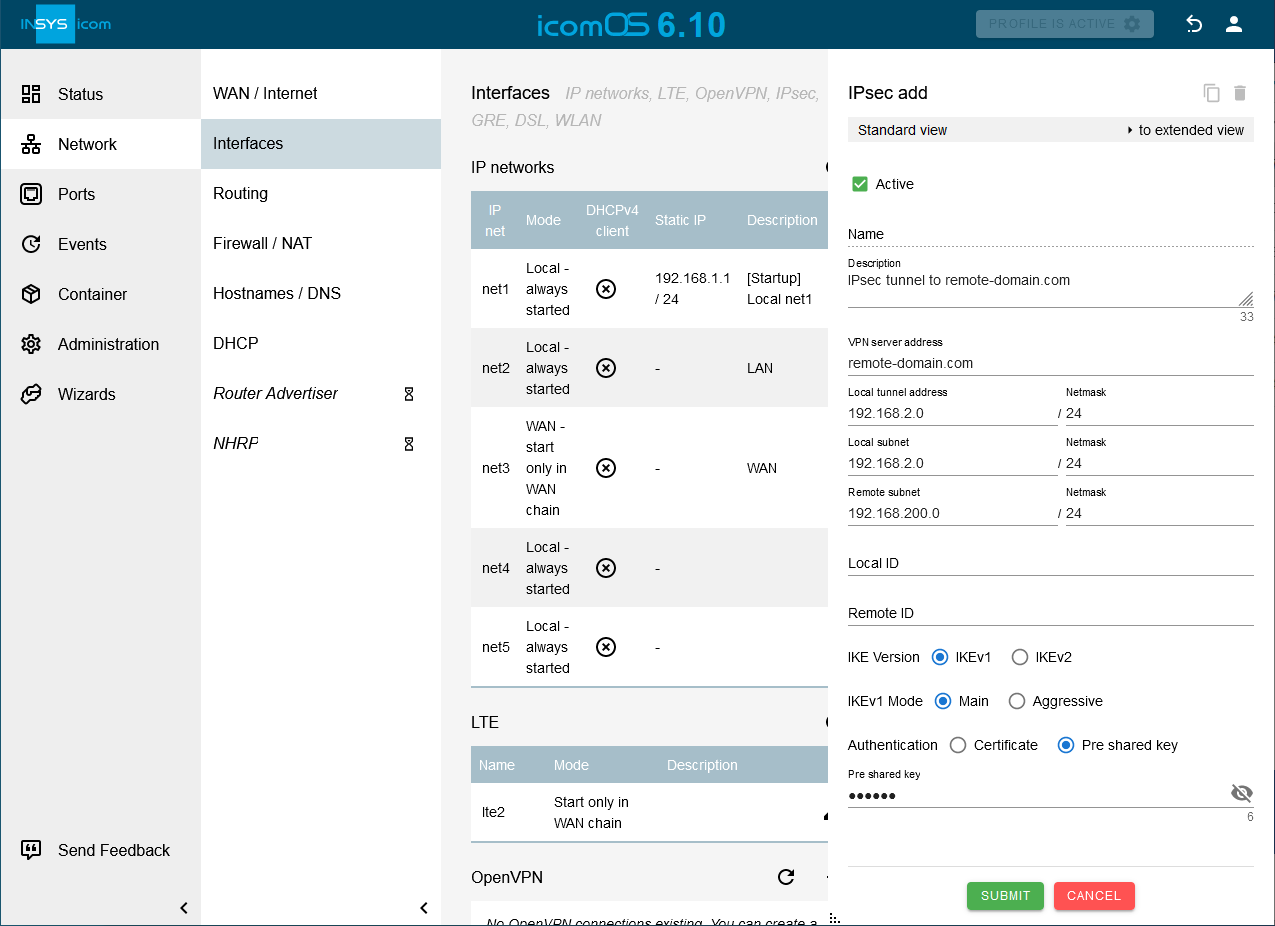
Click on on the Network → Interfaces page under IPsec to add a new IPsec tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec tunnel to remote-domain.com
VPN server address: remote-domain.com
Local tunnel address: 192.168.2.0 / 24
Local subnet: 192.168.2.0 / 24
Remote subnet: 192.168.200.0 / 24
Configure authentication and encryption according to the settings of the remote router.
This adds an interface for an IPsec tunnel from the local LAN to the remote router
All addresses are exemplary for the present example and must be adjusted to your application.
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Interfaces page under GRE to add a new GRE tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: GRE tunnel to remote router
IP address or domain name of remote site: 192.168.200.1
Own IP address: static 192.168.2.1
Local tunnel address: 10.10.10.10 / 30
GRE key: Enter a GRE key only if the remote router requires this.
This adds an interface for an GRE tunnel from the local LAN to the remote router
All addresses are exemplary for the present example and must be adjusted to your application.
The local tunnel address can be selected freely, but must be in the same virtual network than the one of the remote terminal.
In rare cases, it may be necessary to adjust the MTU (maximum permissible number of bytes in a packet to be transmitted). The TTL (time to live) of the packet will be decremented by one by every router that it passes on its way. If the value has fallen to 0, the packet will not be forwarded any more. This helps to avoid endless loops for example. By default, the TTL value from the tunnelled packet is used for the GRE packet.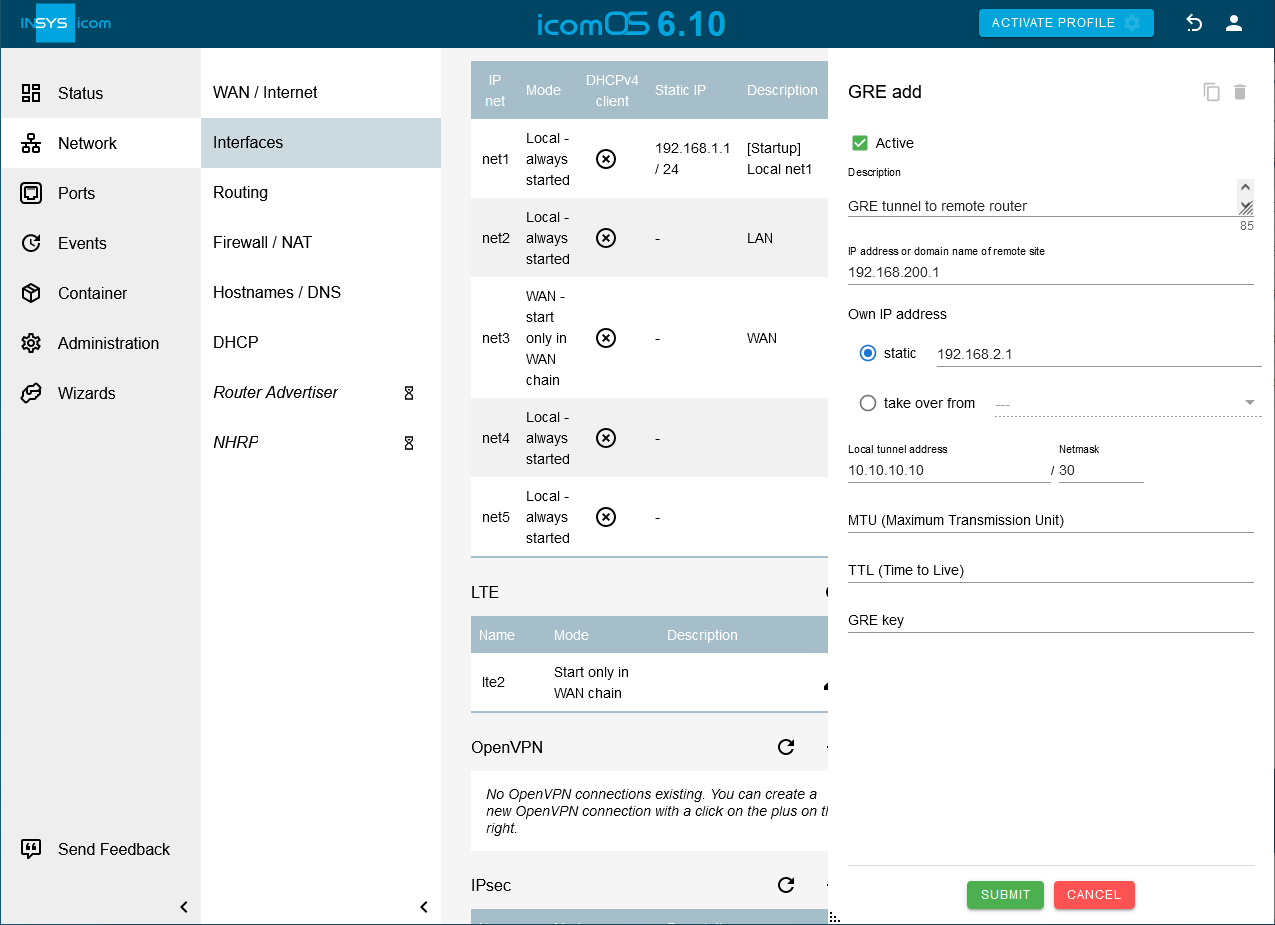
Click on SUBMIT.
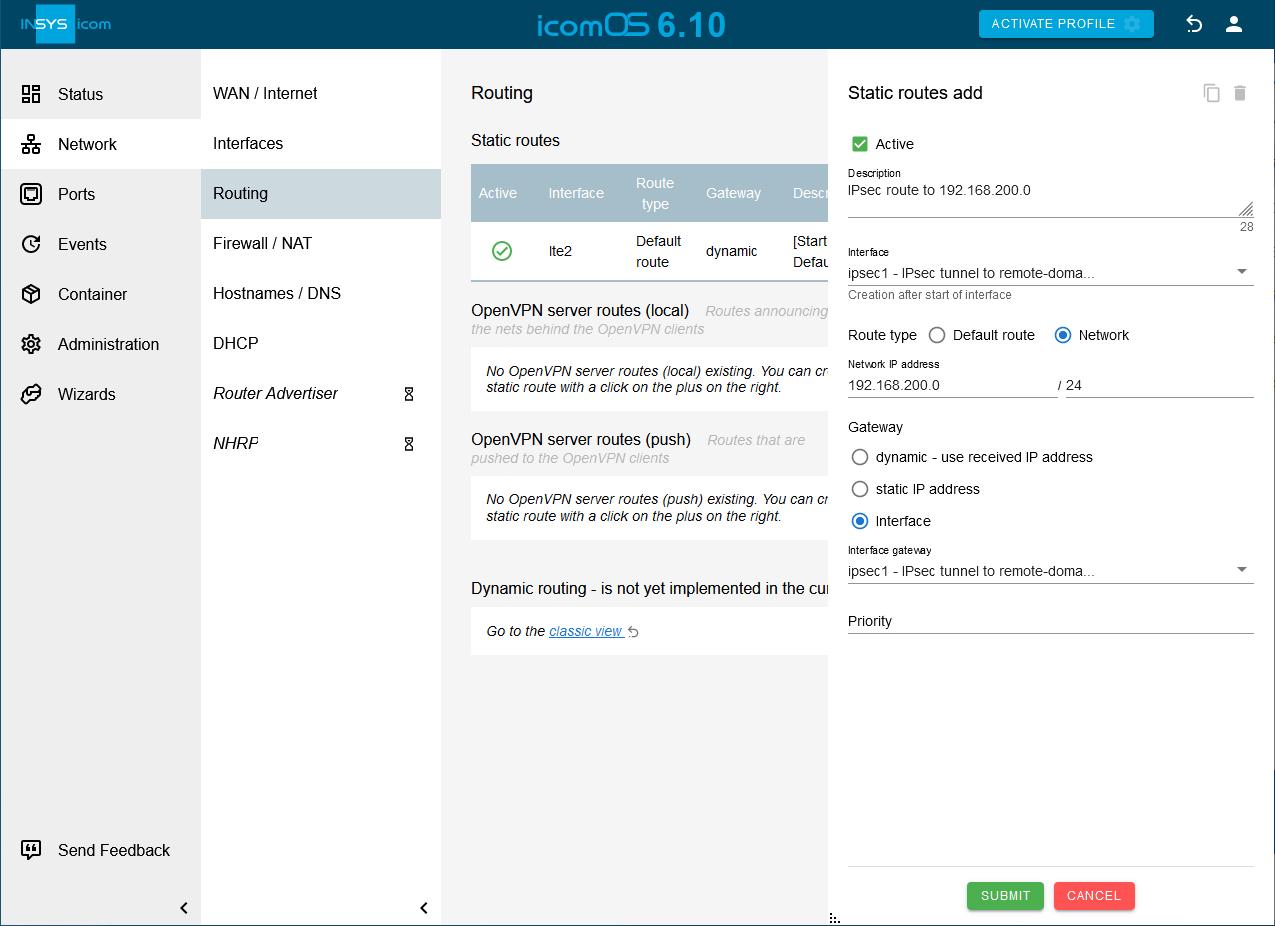
Click on on the Network → Routing page under Static routes to add a new static route through the GRE tunnel to the remote subnet behind the remote router and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec route to 192.168.200.0
Creation after start of Interface: ipsec1
Type of the route: Network 192.168.200.0 / 24
Gateway: interface ipsec1
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Routing page under Static routes to add a new static route through the GRE tunnel to the remote subnet behind the remote router and configure this accordingly:
Description: GRE route to 192.168.201.0
Creation after start of interface: gre1
Type of the route: Network 192.168.201.0 / 24
Gateway: interface gre1
Click on Save settings.
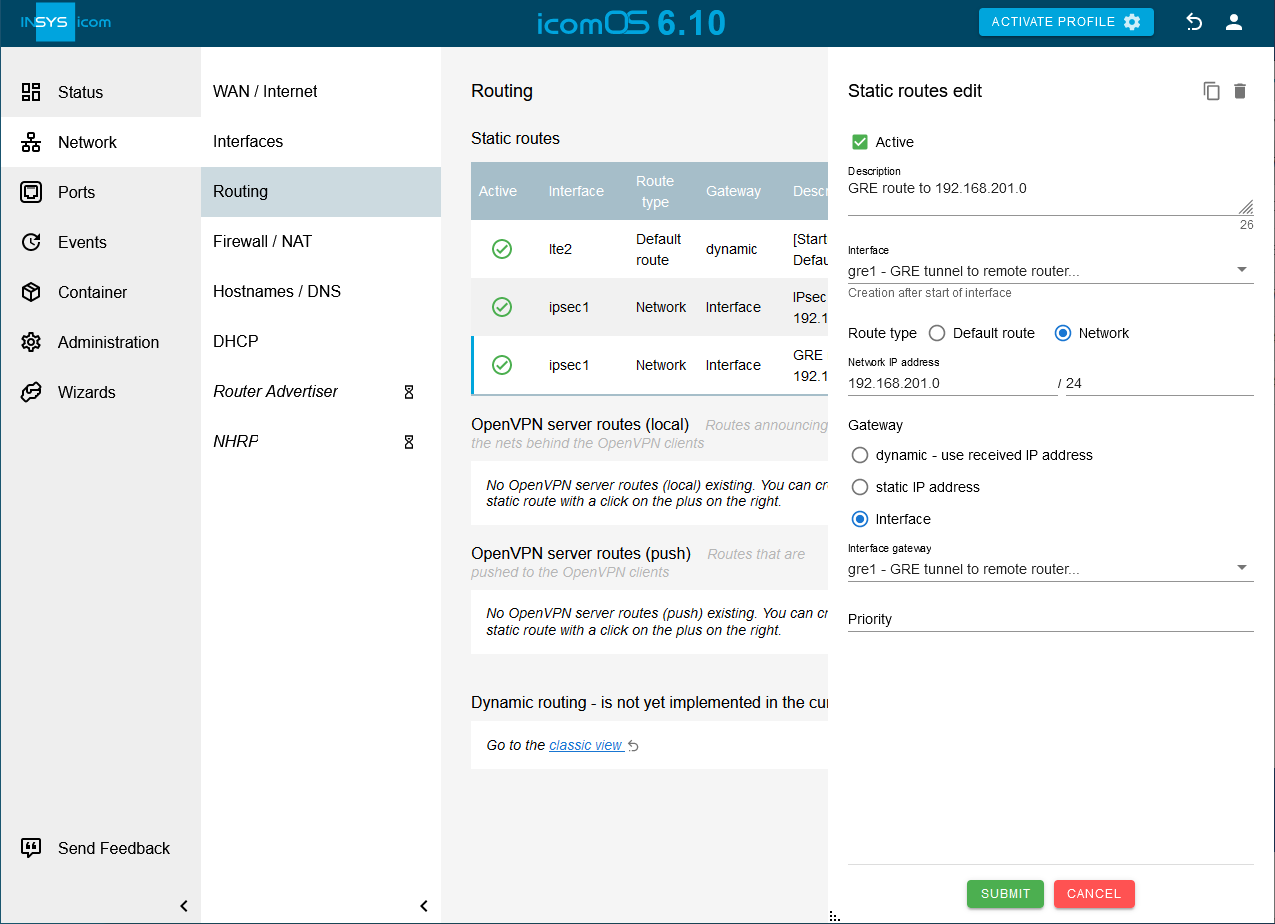
Click on SUBMIT.
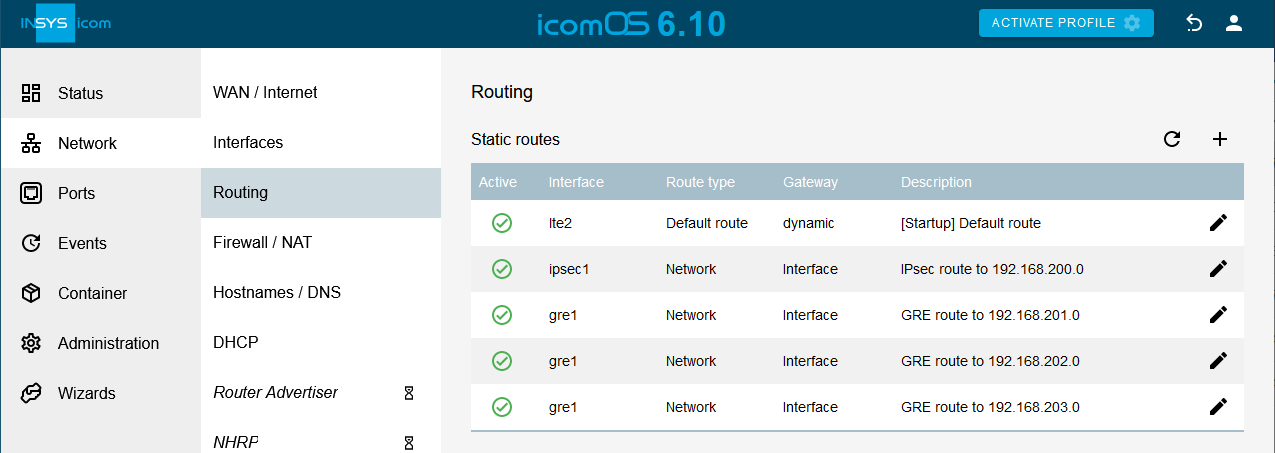
Add the next two routes to the remote subnets 192.168.202.0 and 192.168.203.0 accordingly.
Click on in the WAN chain added by the Startup wizard on the Network → WAN / Internet page to add another interface to the WAN chain.
Select for the interface on Starting position 2 the Interface ipsec1.
Click on again to add another interface to the WAN chain.
Select for the interface on Starting position 3 the Interface gre1.
Please note!
Above two settings add the IPsec and GRE interfaces (in this order) to the WAN chain. A WAN chain is the sequential arrangement of interfaces that defines the establishment of a WAN connection
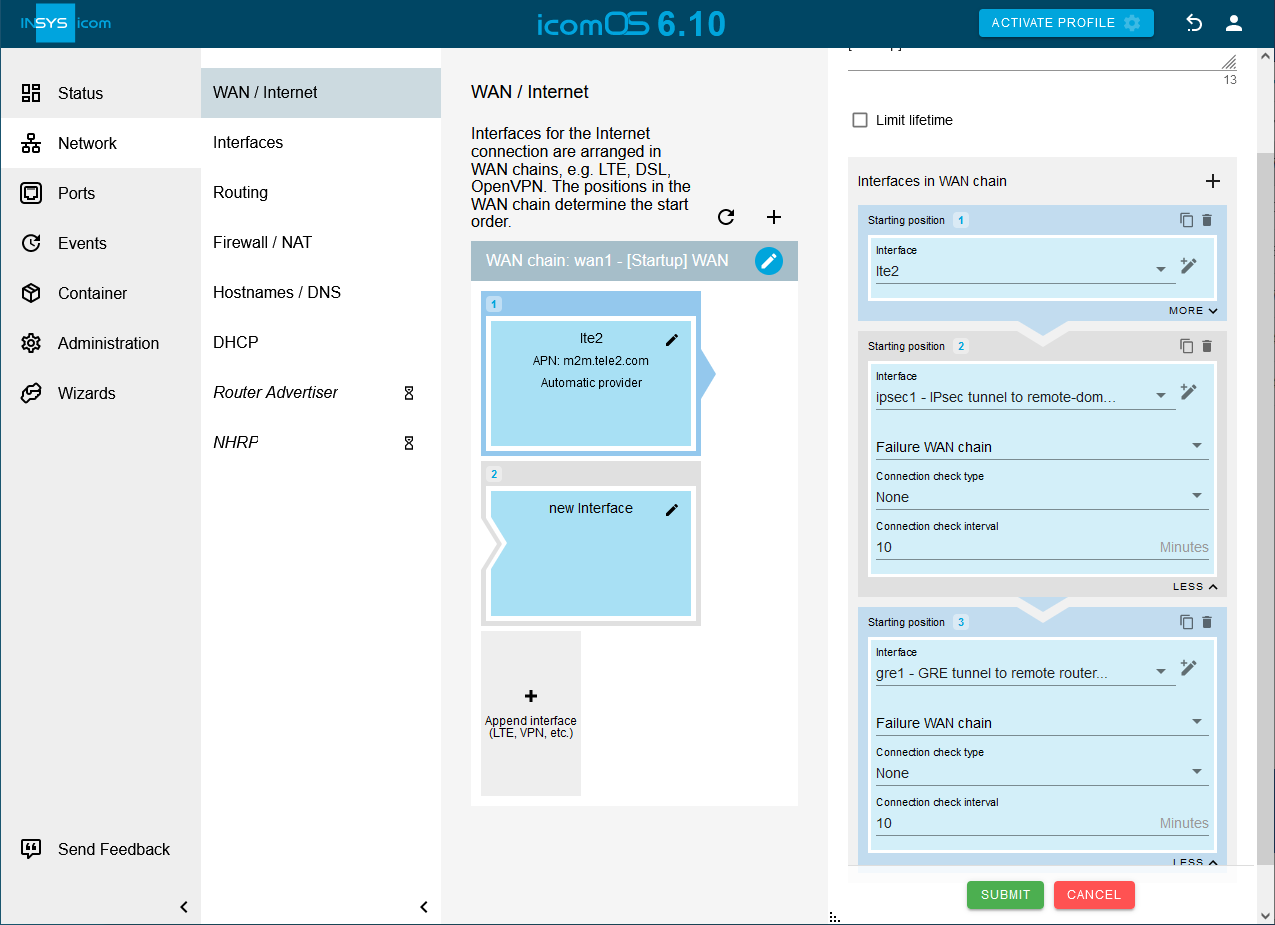
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that rule enables to establish IPsec connections and key exchange and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec (tunnel establishment)
Packet direction: OUTPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: UDP
Output interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Destination port: 500
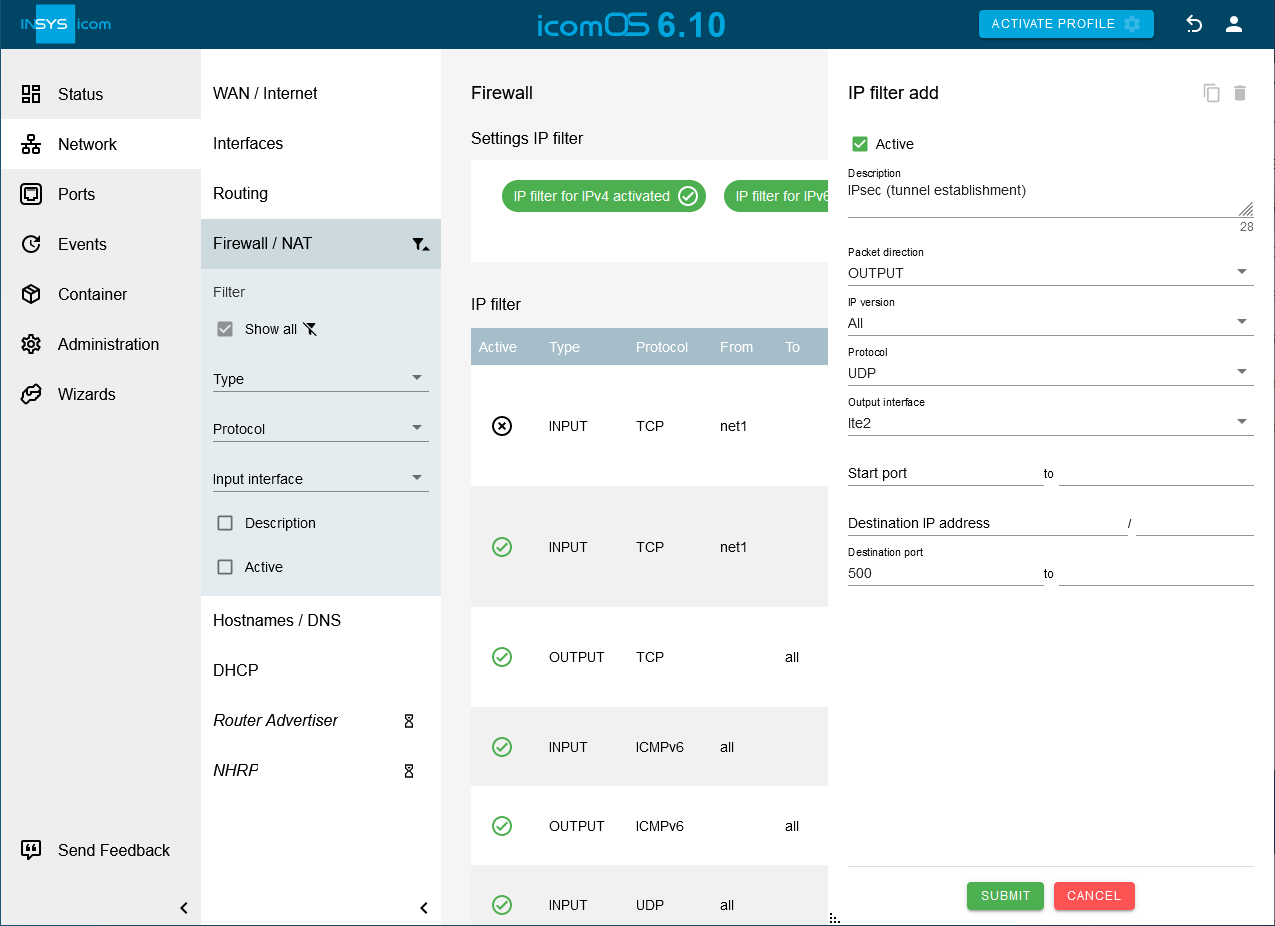
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to establish the IPsec tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec protocol ESP
Packet direction: OUTPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: ESP
Output interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to establish IPsec connections and key exchange when using NAT traversal and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec UDP Port 4500 (NAT traversal)
Packet direction: OUTPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: UDP
Output interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Destination port: 4500
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that rule enables to establish IPsec connections and key exchange and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec (tunnel establishment)
Packet direction: INPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: UDP
Input interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Destination port: 500
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to establish the IPsec tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec protocol ESP
Packet direction: INPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: ESP
Input interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to establish IPsec connections and key exchange and configure this accordingly:
Description: IPsec UDP Port 4500 (NAT traversal)
Packet direction: INPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: UDP
Input interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Destination port: 4500
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to send all data through the IPsec tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: Traffic through the IPsec tunnel sent by the router
Packet direction: OUTPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: All
Output interface: ipsec1
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule enables to receive all data through the IPsec tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: Traffic through the IPsec tunnel sent to the router
Packet direction: INPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: All
Input interface: ipsec1
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to establish the GRE tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: GRE (tunnel establishment)
Packet direction: OUTPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: GRE
Output interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to establish the GRE tunnel and configure this accordingly:
Description: GRE (tunnel establishment)
Packet direction: INPUT
IP version: All
Protocol: GRE
Input interface: Check the WAN interface used, i.e. lte2 or net3.
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule tenables to route all data from the local networks through the GRE tunnel. and configure this accordingly:
Description: Traffic from the local net through the GRE tunnel
Packet direction: FORWARD
IP version: All
Protocol: All
Input interface: net1, net2
Output interface: gre1
Click on SUBMIT.
Click on on the Network → Firewall / NAT page under IP filter to add an IP filter rule that enables to route all data through the GRE tunnel to the local networks and configure this accordingly:
Description: Traffic through the GRE tunnel to the local net
Packet direction: FORWARD
IP version: All
Protocol: All
Input interface: gre1
Output interface: net1, net2
Click on SUBMIT.
Activate the profile with a click on ACTIVATE PROFILE .
Observe the establishment of the WAN chain containing the tunnels on the
 Status → Dashboard page in the WAN chain section.
Status → Dashboard page in the WAN chain section.Click on the Administration → Debugging page on OPEN DEBUG TOOLS , select the Tool Ping, enter available IP addresses of the remote subnets under Parameter and click on SEND to verify the connectivity.
We’ve prepared the following ASCII configuration file for adding the filter rules in one go instead of entering them one by one as described in detail above. Copy and paste it to your text editor or download it using the link below. Don’t forget to adjust it to your application if required.
The ASCII configuration file will add all filters as above with both possible WAN interfaces that can be created by the Startup wizard, i.e. lte2 and net3.
Refer to Adding a List Parameter to a Profile Using Lua to see how to apply an ASCII configuration file to a profile.
ASCII configuration file
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=IPsec (tunnel establishment)
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=output
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=udp
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_dport=500
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=IPsec protocol ESP
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=output
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=esp
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=IPsec UDP Port 4500 (NAT traversal)
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=output
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=udp
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_dport=4500
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=IPsec (tunnel establishment)
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=input
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=udp
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_dport=500
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=IPsec protocol ESP
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=input
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=esp
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=IPsec UDP Port 4500 (NAT traversal)
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=input
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=udp
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_dport=4500
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=Traffic through the IPsec tunnel sent by the router
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=output
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=ipsec1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=Traffic through the IPsec tunnel sent to the router
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=input
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=ipsec1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=GRE (tunnel establishment)
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=output
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=gre
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=GRE (tunnel establishment)
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=input
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=gre
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=lte2,net3
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=Traffic from the local net through the GRE tunnel
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=forward
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=net1,net2
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=gre1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule.add
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_active=1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_description=Traffic through the GRE tunnel to the local net
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_direction=forward
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_protocol=all
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_input_if=gre1
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_output_if=net1,net2
netfilter.ip_filter.rule[last].rule_ipversion=allTroubleshooting
Disable the IP filters for IPv4 in the Network → Firewall / NAT menu under Settings IP filter to check whether incorrect filter settings are the reason for connection problems.